Raspberry Pi Remote Access: Ultimate Guide & Solutions
Are you ready to unlock the full potential of your Raspberry Pi from anywhere in the world? Transforming your Raspberry Pi into a remote workstation is not just a possibility; it's a readily achievable feat, opening doors to unprecedented control and flexibility.
In an era defined by remote work and decentralized access, the ability to control your devices from afar has become invaluable. The Raspberry Pi, a marvel of compact computing, stands at the forefront of this revolution. Its small size and affordability are only a prelude to its immense capabilities as a versatile computing platform. From building hardware projects and automating your home to delving into industrial applications and exploring the intricacies of the Internet of Things (IoT), the Raspberry Pi has proven itself to be an indispensable tool for tech enthusiasts, hobbyists, and professionals alike.
One of the most compelling aspects of the Raspberry Pi is its ability to be accessed remotely. This capability allows you to tap into the device's power and functionality from anywhere in the world, provided you have an internet connection. This remote access unlocks a world of possibilities, from managing your home automation system while on vacation to troubleshooting a project from a different city. But how do you achieve this remote access? What are the tools and techniques needed to transform your Raspberry Pi into a remote workstation thats ready to respond to your commands, regardless of your location?
Before we delve into the intricacies of remote access, its important to have a basic understanding of the Raspberry Pi itself. In its simplest form, the Raspberry Pi is a pocket-sized computer that runs on the Linux operating system. Its a multifaceted device, capable of handling a wide range of tasks. Its versatility makes it suitable for a variety of applications. Whether you're a student learning programming, a maker building electronic projects, or a professional seeking remote access to a specialized system, the Raspberry Pi offers a unique and affordable solution. The official documentation for Raspberry Pi computers and microcontrollers provides a wealth of information and resources for users of all levels.
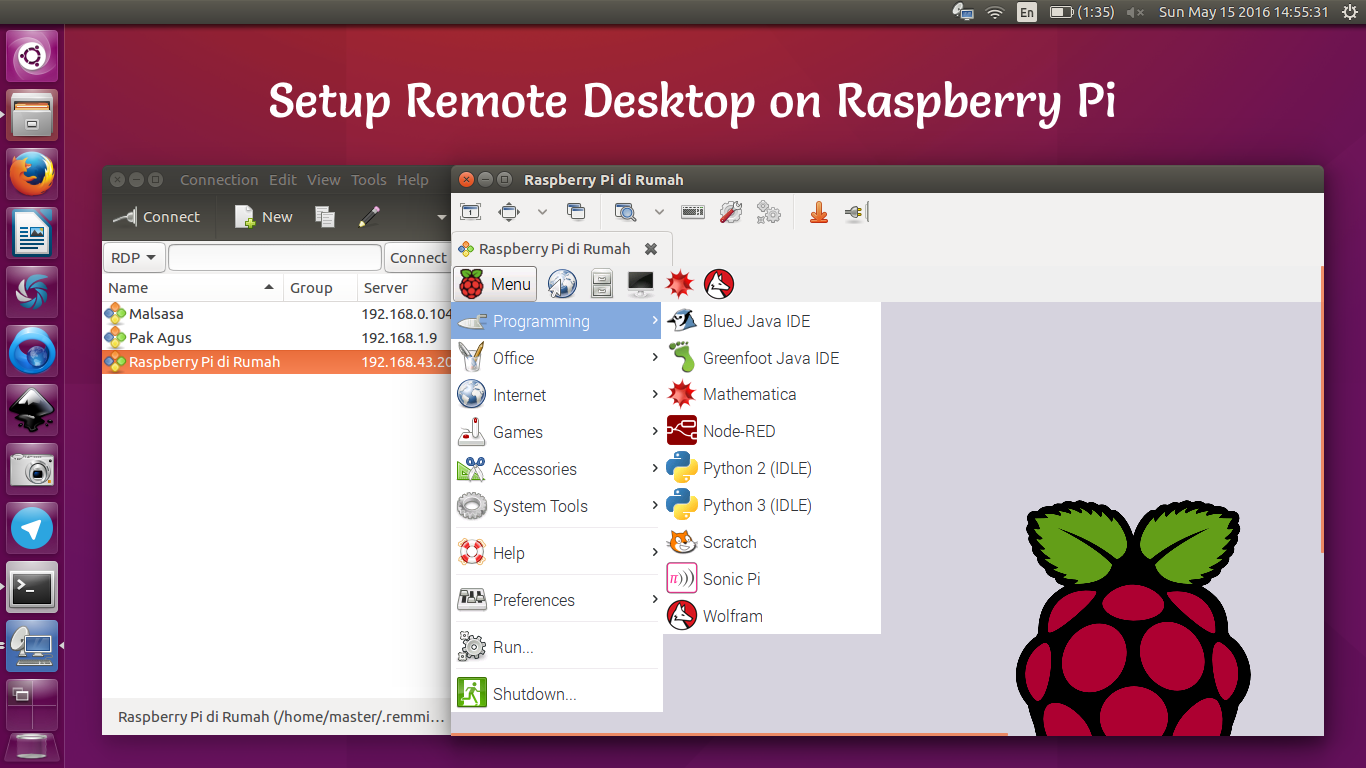
One of the first methods to explore is Virtual Network Computing (VNC). VNC is a simple protocol that gives you remote access to graphical user interfaces. Think of it as a window into your Raspberry Pi's desktop. You can see and interact with everything on the screen, as if you were sitting right in front of it. To set up remote desktop access on your Raspberry Pi, you will need to install a VNC server. This server acts as the intermediary, allowing your remote device to connect and control the Pi's desktop. VNC (Virtual Network Computing) allows you to access the desktop of your raspberry pi from another computer or mobile device.
However, VNC is not without its limitations. In many setups, it is limited to a local network. This means that you can only access your Raspberry Pi remotely if you are on the same network. While this is convenient for home use, it restricts access when you are away from your local network. There are ways around this limitation, such as setting up a Virtual Private Network (VPN) for your network, or port forwarding. Another option to explore is the use of RealVNC Connect, which offers a complete package thats perfect for Raspberry Pi users. The combination of RealVNC server and RealVNC viewer gives you seamless access thats both secure and reliable.
For those who prefer a command-line interface, SSH (Secure Shell) offers a direct and secure way to access your Raspberry Pi. While not allowing for direct graphical access, SSH provides a robust and efficient method to manage the system, run commands, and transfer files. In a previous post, we saw how to set up Wi-Fi on the Raspberry Pi and how to wirelessly connect to it via an SSH client, such as PuTTY. PuTTY is a great way to access the command line, but you cant use it to access the desktop. To connect to the Raspberry Pi from a Windows machine, follow these steps: Press the Windows key + R, type `mstsc`, and press Enter to open the Remote Desktop Connection. Then, enter the necessary credentials to connect.
Now, let's delve into the practical steps required to set up remote desktop access. This involves installing a VNC server on your Raspberry Pi and configuring your network to allow remote connections. If you are new to the world of Raspberry Pi, dont worry; transforming your Raspberry Pi into a versatile remote workstation can be achieved in under 30 minutes, a testament to the user-friendly design of the operating system and the efficiency of the configuration process. This guide walks you through the essential steps.
One of the popular choices for remote desktop access is XRDP, an open-source implementation of the Microsoft Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP). This protocol allows you to connect to your Raspberry Pi from a Windows machine, using the familiar Remote Desktop Connection tool. To get started, youll need to install XRDP on your Raspberry Pi OS. Then you can enable the service using systemctl. The official documentation for Raspberry Pi computers and microcontrollers provides detailed instructions. With XRDP, you can seamlessly connect to your Raspberry Pi from a remote desktop client.
What you want is to either set up a VPN for your network or to port forward your SSH port. The former will require setting up a VPN server on your network. Port forwarding is pretty safe up to the extent that the server software receiving those connections is secure. This brings us to the good news: the process is less complicated than it seems. While there are many solutions, none are perfect (VNC is limited to a local network, TeamViewer is a commercial product, etc.). But setting up remote desktop access offers a good balance of security and functionality.
To make the process easier for you, I will show you some methods, including how to set up VNC. Then, I'll delve into other considerations to optimize your setup. This detailed walkthrough will help you set up the system and the key steps to keep in mind.
Beyond the technical aspects, it's important to understand the ethical and security implications of remote access. Always ensure that your network and the server software receiving the connections are secure. It's always wise to use strong passwords, keep your system updated, and consider implementing additional security measures. Accessing a Raspberry Pi remotely from a different network using Windows 10 is a powerful skill for tech enthusiasts, hobbyists, and professionals alike. If you are looking for more in-depth information or a visual guide, I have a video lesson available for the community members. You can join here and watch it directly if you are interested (with 20+ other lessons for Raspberry Pi and many other benefits).
Connecting to a Pi remotely has always been interesting. The compact size and affordability of the Raspberry Pi belie its immense capabilities as a versatile computing platform. Its small form factor and low cost make it suitable for learning programming, building electronics projects, automating your home, and much more.
Lets also consider the exciting world of the author, who goes by the enigmatic pen name howchoo. Mysterious and multifaceted, howchoo has emerged as a captivating storyteller, leaving readers mesmerized by the uncharted realms they craft with their words. As a creative persona, howchoo embodies the spirit of boundless curiosity and limitless creativity. The official documentation for Raspberry Pi computers and microcontrollers can offer further reading.
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Operating System | Linux (typically a Debian-based distribution like Raspberry Pi OS) |
| Processor | Varies by model; typically an ARM-based processor |
| Memory (RAM) | Varies by model; typically 1GB, 2GB, 4GB, or 8GB |
| Storage | MicroSD card (for the operating system and data) |
| Connectivity | Ethernet, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth (depending on the model) |
| Ports | USB ports, HDMI port, GPIO pins, audio jack (depending on the model) |
| Remote Access Protocols | VNC, SSH, XRDP (Remote Desktop Protocol) |
| Common Applications | Hardware projects, Home automation, Industrial applications, IoT (Internet of Things), Remote access, Educational purposes |
| Advantages | Small form factor, Low cost, Versatile, Energy-efficient, Large community support |
| Disadvantages | Performance limitations compared to desktop computers, Storage dependent on microSD card |
| Official Documentation | Raspberry Pi Official Documentation |
In conclusion, whether you're seeking to build a versatile home automation system or simply want to access your projects from anywhere in the world, the Raspberry Pi offers a flexible, affordable and exciting way to interact with technology. Its potential is limited only by your imagination.